I only have the barest understanding of Japanese, and the auto-translation on this video is pretty bad*, but I still found this Japanese Youtuber’s experience with the Steam release of Epyx Rogue to be interesting (27 minutes):
They keep using terms from Chunsoft’s Mystery Dungeon games, especially Torneko no Daibouken from the Super Famicom, but seem to have a good sense of how those items connect to and were inspired by Rogue.
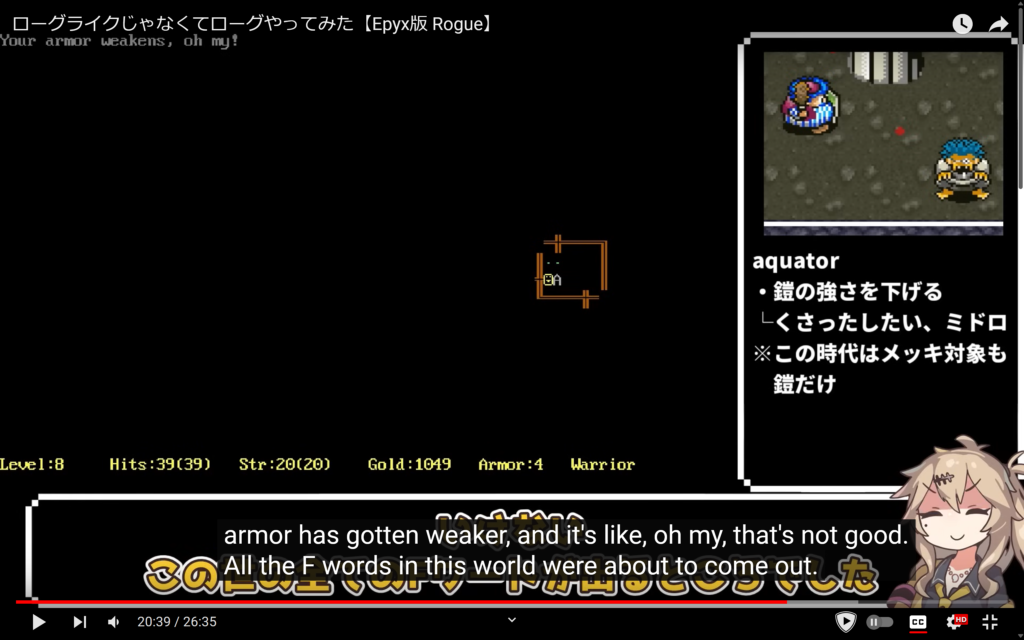
They also die a lot. Because Rogue doesn’t want you to win. It was made for a community of players who would play it over and over, and were competing on shared scoreboards on university machines, and indefinite play makes for a poor measure of player skill. Standing and trading blows with every monster is a bad strategy in Rogue in the long run. Instead, it helps to run from strong enemies, to build up more hit points so as to defeat them, and sometimes in order to escape them to the next floor. Rogue’s monsters grow in strength as you descend fairly quickly, and the player is usually not far ahead of them in the power curve. Then around the time Trolls show up they’re roughly an even match, and they keep getting tougher. The point where the monsters become stronger than the player is different every game, and depends a lot on which items the player has found and has identified, but it always comes eventually. They eventually get pretty far, dying on their fifth attempt to a Griffin on Level 18.
*
“Water supply texture: Say goodbye to the smell of raw oysters.”
“The Dora doll’s twisty honey positive is getting warmer.”
“I miss the days when I used to go Hee Hee in Centauros.”
“Let’s quickly wash and throw away the rotten plastic bottles we drank from.”
Tell me more, auto translate bot!