Another personal project post! I have done more work in making David Caruso II’s obscure Commodore 64 CRPG Dungeon, published in the issues of the disk magazine LOADSTAR more than once, presentable to current-day audiences. Although it certainly has its limits, there are some aspect to it that are unique, even forward-thinking. We posted about Dungeon here before. To remind everyone, we sell Dungeon on my (rodneylives’) itch.io page for $5, with the blessing of rights-holder and LOADSTAR owner Fender Tucker.
There are a few bugs in Dungeon, now basically impossible to fix, that I’m trying to track down and document, and I’m also working on improving the documentation, as well as provide some useful goodies with the system, like a disk of monsters, equipment and magic items. That’s useful because Dungeon has a special feature where it’ll take the monsters and items on a “Data Disk,” and scatter them around a dungeon map of its own creation. It calls these randomized adventures “Lost Worlds.”
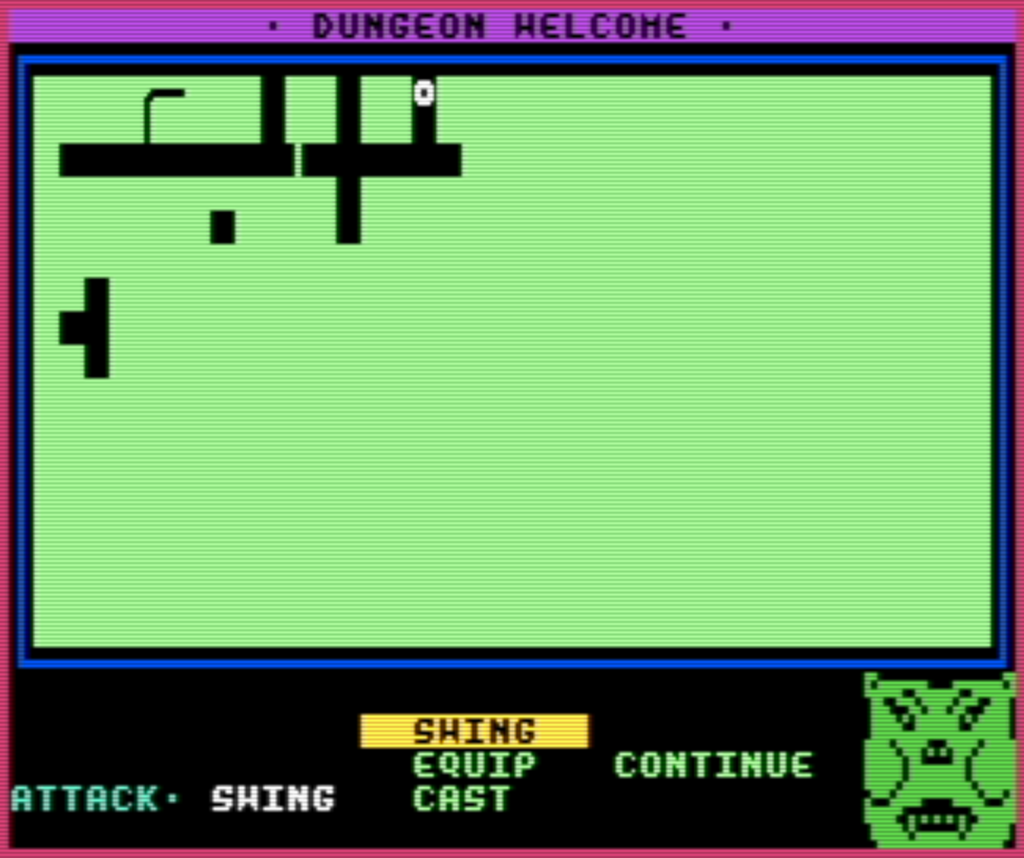
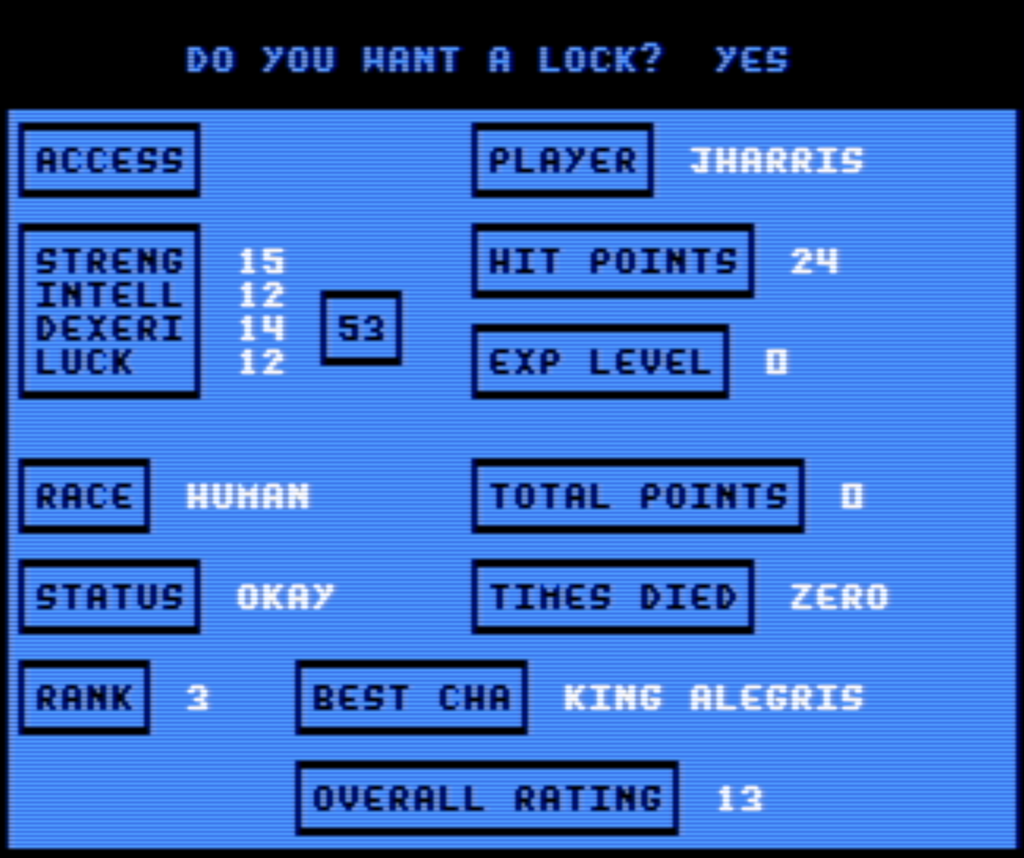
Lost Worlds operate as a kind of quasi-roguelike. The Dungeon software creates a random map and places random items around it, but once created it becomes a Dungeon adventure that any created character can explore as many times as they like. While it doesn’t have roguelike tactical combat gameplay or random item identification, it does have a form of permadeath. Characters only get three lives to advance their level as far as they can go.
Lost Worlds are interesting places to explore, but there are some bugs in them. It is possible, in fact pretty easy, to get stuck in a part of the dungeon from which one can’t escape. Sometimes a one-way door leads into an area that can’t be escaped, and sometimes a passage-blocking trap will strand the player’s character in a dead-end. And once in a while a Lost World is downright unfinishable, its goal item disconnected from the parts of the dungeon the player can even reach.
While there are spells (Passwall and Teleport) that can release a trapped character, if they aren’t available the character is not completely lost. If you turn off the C64 (or close the emulator), then return to the Guild screen, the character will be marked as GONE. Over time, measured in loads of the Guild menu, the character will eventually find their way back on their own. It takes quite a while for this to happen though: I counted 15 loads, saving the game each time, before a GONE character returned.
This video (23 minutes) is is something I recorded myself as a demonstration of both Dungeon’s gameplay, and its Lost World adventure generation. It uses a set of 30 low-level monsters and items based on the stats of the old Basic edition of D&D, and a set of magic items I created for usefulness and to show off Dungeon’s spell set.
So, why would someone want to play this game, when there’s so many other newer CRPGs out there to play?
- The idea of rolling up a character and taking them through scenarios made by other people, to try to get their level up as high as they can get before they die three times, is great. My hope, perhaps misplaced, is this release will inspire other people to make dungeons for others to play, and I look forward to seeing them myself.
- The magic system of Dungeon, while it doesn’t allow for characters to learn spells themselves, is unique in that most of the spells are utility spells! There are spells for passing through walls, for teleporting anywhere on the map, for revealing terrain, for seeing in darkness, for giving oneself a damage shield, for locating the goal item, for disarming traps, and more. There is only one direct damage attack spell! Spells are more like tools than something you use to pound through the enemies.
- The dungeon model allows for dark areas, traps that block exits, two-way and one-way teleporters, secret doors, one-way doors, and decorating dungeon maps with PETSCII graphics. The simplicity of the dungeons, all of them fitting on one screen, works in Dungeon’s favor. No dungeon can be too large since they must all fit within the bounds of the map grid.
There are unique design considerations for making Lost Worlds too. Even though the computer creates the maps unaided, since it populates them from the monsters, items and traps that are on the Data Disk, the difficulty of the resulting dungeon is affected. The various doodads are distributed without apparent heed for what they are; I wonder if the generator actually cares for their identities or if it just checks how many of each type are on the disk, so as not to exceed that number.
If there are more easy monsters, more powerful items, and more weak traps on the disk then the dungeon will be easier due to their corresponding numbers being greater, and vice versa. It occurs to me that one of the flaws in the dungeon generation I mentioned could be alleviated, by not giving it one of the wall creating traps that could trap a player in a dead-end, but that also makes the dungeon a bit less interesting, so I’ve left it in the mix I use.
I recognize that, if I let myself, this might become a Dungeon blog. Rest assured, I’m not going to take it that far. But I really hope that some people give Dungeon a chance. While sure it has its inspirations (one person on Mastodon said it reminds them of Phantasie, a somewhat less obscure early CRPG), I think it’s pretty unique, and deserves for more people to have a look at it. I’m particularly pleased how well the sample monsters and items I made work in the Lost World framework, and I’m trying to think of ways that it might be improved. More on this later… but, not immediately, I think.