Is that hyperbolic? It probably is. But the heart wants what it wants, and what mine wants is CP/M for the MOS 6502 processor. Set Side B is a blog about computer entertainment, in all its many forms, and this qualifies in my mind, because it’s not like anyone’s going to be using it do real work. Right?
I found out about it through the (mostly) wonderful blog The Oasis BBS. It’s called CP/M 65, and it was made possible when CP/M’s source was opened in 2022. Wait, maybe I should explain what CP/M is. Sure, it has a Wikipedia page, but I like explaining it.
Gary Kildall created CP/M, “Control Program for Microcomputers,” for the Z80 microprocessor, and it became the first widely-used standard OS for home computing. Its importance and influence cannot possibly be overstated: PC-DOS (later known as MS-DOS) was created as a clone of CP/M for the 8086 processor, meaning, the reason .COM files are still technically considered executables, and why we still have drive letters in Windows 11, are both directly because of CP/M.
A case could be made that, if IBM hadn’t made the IBM PC out of standard parts, making possible the huge market for clone machines, it’d still be a CP/M world today, in some way. It was the first standard OS, one where it ran on machines made by more than one manufacturer. Many of the CP/M machines companies, the Kaypros and Osbournes, are gone now, but they had quite a large niche at one time.

Commodore released a CP/M cartridge for the Commdore 64, an amazingly ridiculous and rare package because the C64 used a 6502 processor. The cartridge worked only because it contained a Z80 processor inside itself, and put the 6502 in the system to sleep to do work. It ran much more slowly than other CP/M systems, and on top of that it still had to use Commodore’s 1541 disk drive, a fatal flaw, because it meant that while it could run CP/M software, it couldn’t read the disks that had them, because CP/M’s native disk format couldn’t be read by the 1541’s read heads. (The C128 had a built-in Z80, and the 1571 disk drive that was made for it could read CP/M disks natively, but by that time CP/M was already dying, pushed out by the PC standard and all those clones I mentioned.)
This thing I’m posting about, CP/M 65, has no relationship to that woeful product. It’s a port of CP/M to the 6502 processor. It can’t run Z80 CP/M software. But in all other senses, it is CP/M. What that means is that it has its own BIOS.
CP/M’s BIOS is what allowed its software to run machines made by different manufacturers. The BIOS acted as a translation layer between the hardware and the software. Programs wouldn’t interact with the hardware directly, but instead make calls through the BIOS whenever they needed to use some part of the hardware, like when it needed to access the disk or output characters to the screen. The result was that unless the software was written specifically to take advantage of a computer’s specialized hardware anything extra it had would go unused, but it also meant that a software developer could write one program and, so long as it restricted itself to interacting with the system through that BIOS, it could run on any CP/M machine that could read the disk.
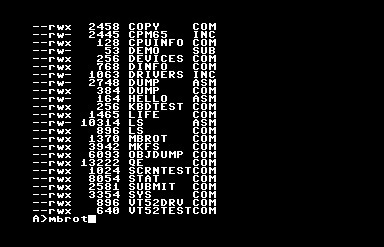
CP/M 65 provides such a BIOS for all of its supported platforms, and as a result, while using it will give you a plane-jane, character-mode program, it’ll let you write a program that will run on any of them. Indeed, since this version of CP/M supports relocating executables, its programs can run on a much wider variety of hardware than original CP/M could. You can write a single program that can run on a Commodore 64, VIC-20, BBC Micro, Atari 8-bit, Apple II, KIM-1(!) and, if you can find the incredibly obscure keyboard and disk drive hardware for it or else emulate them, the Super Nintendo Entertainment System(!!).
But on a C64 it shines slightly more than the others, because it has integrated fastload routines, meaning that it gets around the C64’s greatest flaw, its horribly slow disk drive.
So this basically means now 6502s have their own cross-platform version of DOS, or something a lot like it. It has little software, but it does have an assembler, and a version of BASIC, and if you don’t mind writing it on a (pah!) modern computer, you can also write programs for it in other languages.
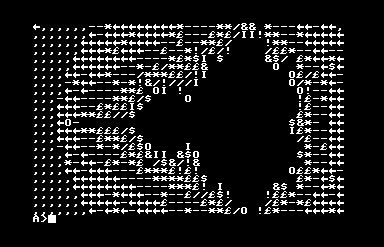
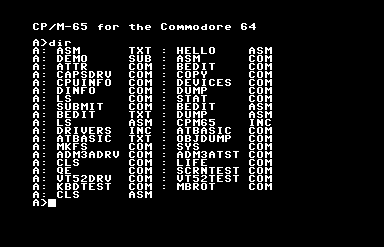
If you want to try this wonderfully misbegotten thing, something like Frankenstein’s Monster wearing a ribbon, its GitHub is here, and you can find binary release disk images here. The one with the extension .d64 is the C64 version, and it loads right up in the Commodore computer emulator VICE, although I found out it’ll fail to boot unless you turn on “True Disk Emulation” for Drive 8. But it works! It comes with an assembler and BASIC, and a vi-like text editor, an implementation of Conway’s Life, and even a Mandelbrot set plotter. I kind of want to write software for it!
CORRECTION: Silly me, here I was assuming that CP/M 65 itself was a fairly recent thing, but as it turns out it’s been around for around 30 years!
CORRECTION FOR THE CORRECTION: Well the guy working in this very long Youtube playlist (maybe 31 hours?) created it in 2022, which isn’t 30 years ago. Ah well!